This Chart Demonstrates That The Marginal Cost
So the equilibrium will.
This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost. This chart shows that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases. For unlimited access to Homework Help a Homework subscription is required.
Public property is land or goods. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost. Employees needed to manufacture a good.
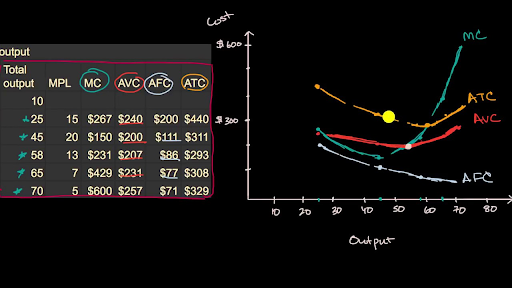
For example if I have a firm that produces chocolate and my daily output is 10 bars of chocolate per day. For example if I have a firm that produces chocolate and my daily output is 10 bars of chocolate per day. Initially decreases as production incr.
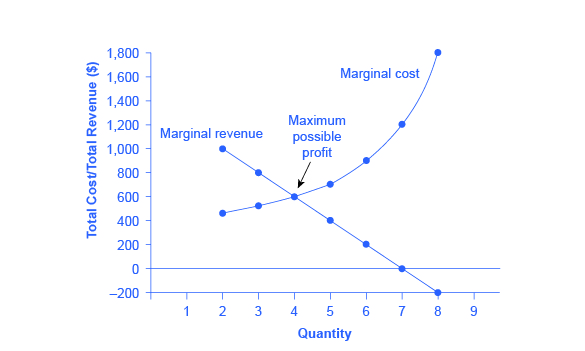
Questions in other subjects. The second column is labeled Total cost with entries 0 1 150 175 225 350 5. THIS IS THE BEST ANSWER.
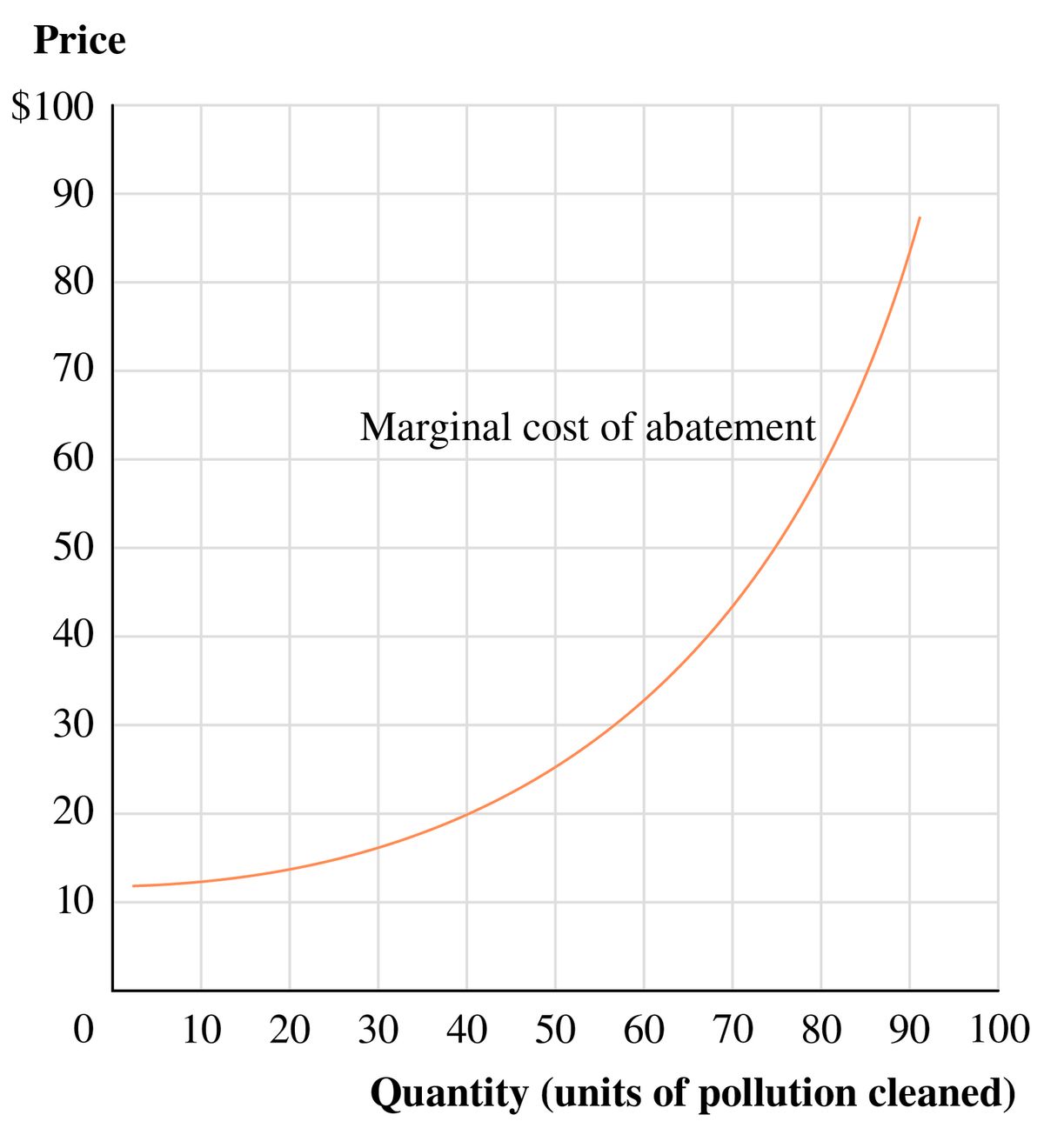
A country decides to create goods at half the cost of another country. The chart shows the marginal cost of producing apple pies. Marginal Cost refers to the cost of producing an additional unit of an item.
This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost A. The graph of pie production initially the marginal cost is decreasing up to the third pie. The average temperature at the south pole is -4962and the average temperature at north pole is -3468.
The factors of production include the number of. A initially decreases as production increases. What is the role of the three questions of.
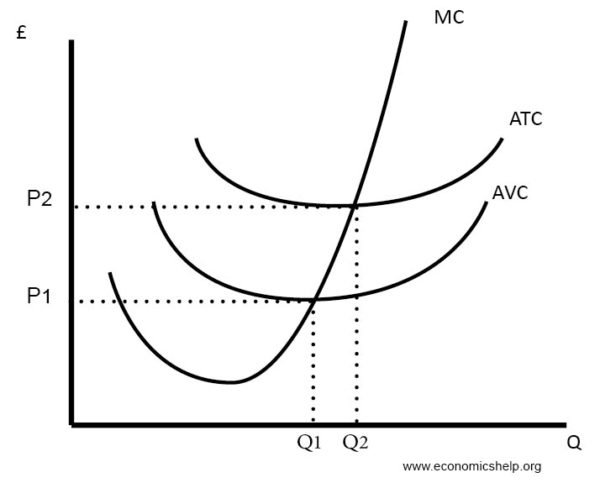
As production increases marginal costs will initially decrease. In a perfectly competitive market long-run equilibrium will occur when the marginal costs of production equal the average costs of production which also equals marginal revenue from selling the goods. The second column is labeled Total cost with entries 0 1 150 175 225 350 5.
Owned by an individual. In the short term factors of production such as capital are fixed. The chart shows the marginal cost of producing apple pies.
A 3-column table titled The cost of pie production has 7 rows. Marginal Cost refers to the cost of producing an additional unit of a good. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost.
The first column is labeled Pies produced per day with entries 0 1 2 3 4 5 6. Initially decreases as production increases. The chart shows the marginal cost of producing apple pies.
The chart shows the marginal cost of producing apple pies. Which situation is an example of comparative advantage. Marginal cost is cost if you produce ONE more unit of good.
Initially decreases as production increases. In the short run factors of production like capital are fixed. Eventually decreases as production increases.
Initially decreases as production increases. How much higher is the average temperature at the north pole than at the sou. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases.
As production increases marginal costs will initially decrease. The marginal cost is how much it costs to produce one unit more than I normally produce that is the cost of the 11th bar. The marginal cost content is simple.
D eventually increases as production decreases. The marginal cost is how much it costs to produce one unit more than I normally produce that is the cost of the 11th bar. As the chart demonstrates a markets long-run supply curve is the sum of a series of short-run supply curves in a given market.
Initially increases as production increases. A 3-column table titled The cost of pie production has 7 rows. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost.
The chart below shows the nationwide DUC inventory peaked in spring of 2020 just as prices dived at the onset of the coronavirus pandemic. Marginal cost is cost if you produce ONE more unit of good. B initially increases as production increases.
Economics Midterm Terms.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Law_of_Diminishing_Marginal_Productivity_Oct_2020-01-d3c30a9c6ba442b9bccc7b99158251e3.jpg)

/MarginalRateofSubstitution3-a96cfa584e1440f08949ad8ef50af09a.png)