Enthalpy Of Formation Chart
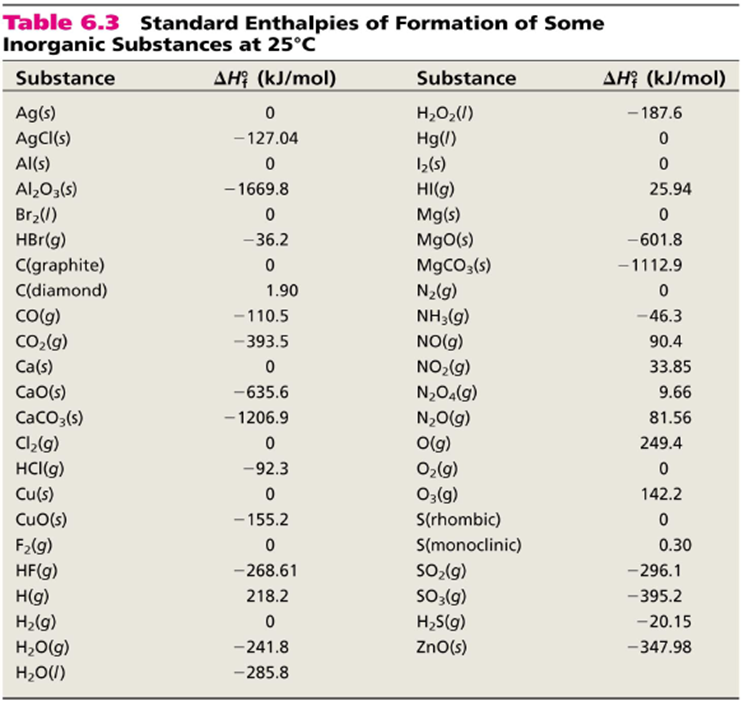
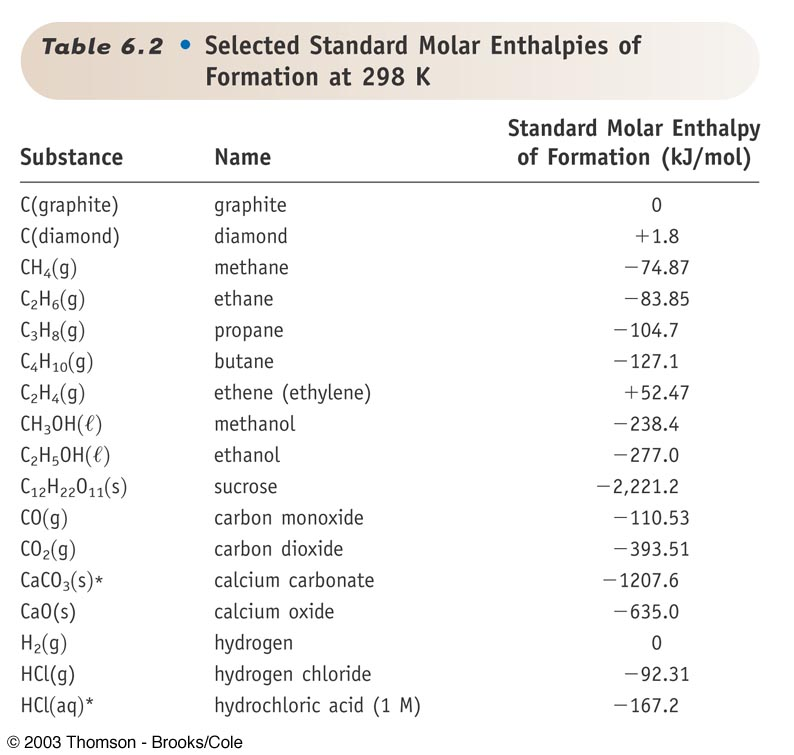
Table 146 shows standard enthalpies of formation.
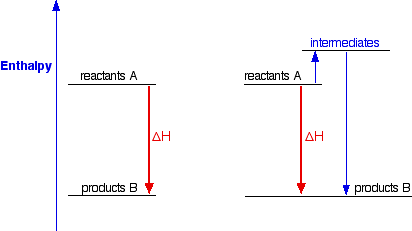
Enthalpy of formation chart. The standard enthalpy of formation ΔH f is an enthalpy change for a reaction in which exactly 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from free elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions. For diatomic molecules enthalpy of atomization is equal to the enthalpy of bond dissociation. ΔH fo A 433 KJmol.
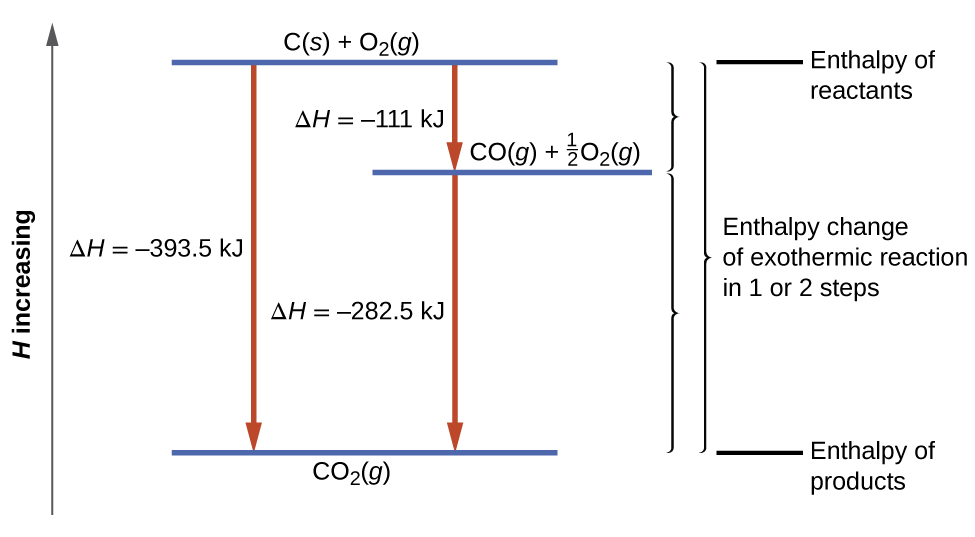
CH 4 g C g 4H g Δ a H 0 16650 kJ mol -1. Standard Enthalpies of Formation Alan D. Check We expect the enthalpy of formation of a stable solid such as calcium carbonate to be negative as obtained.
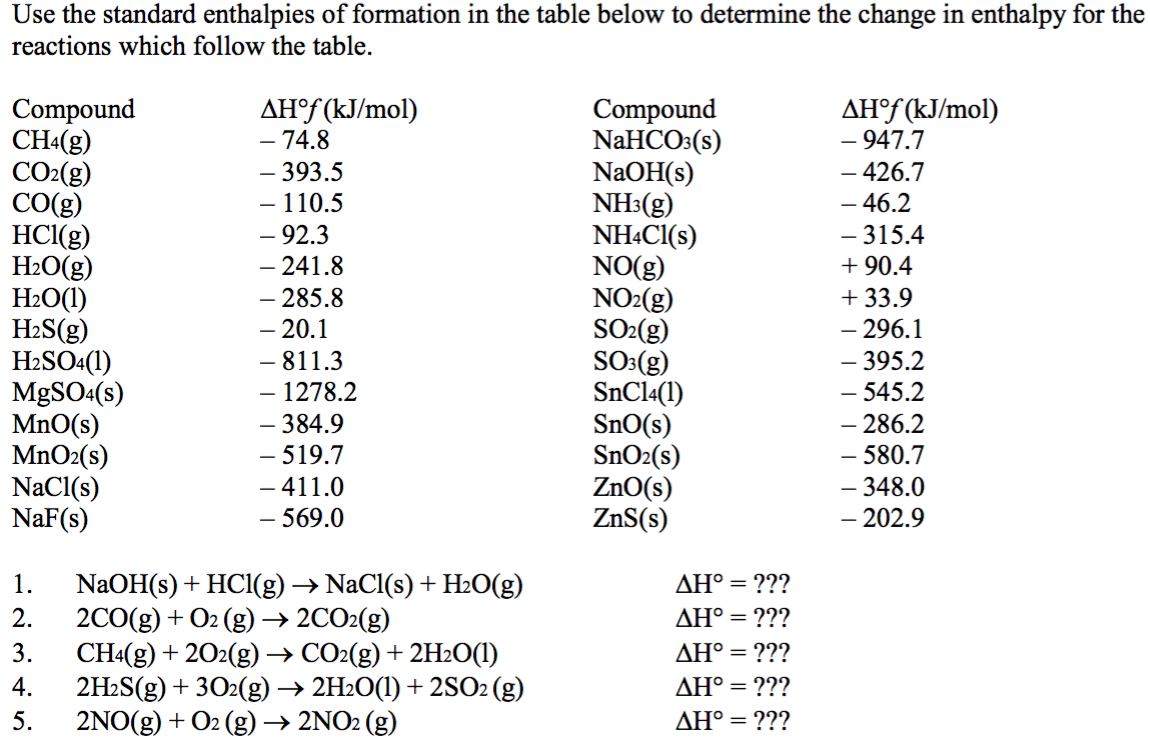
Substance Enthalpy of combustion Hc 0 kJmol Enthalpy of formation Hf 0 kJmol Free energy of formation Gf 0 kJmol Entropy S0 JKmol Hydrocarbons CH4g methane-890 -7481 -5072 18626 C2H2g acethylene-1300 22673 20920 20094. The enthalpy of formation of sulfuric acid is represented by the following equation. Given the following standard enthalpy change use the standard enthalpies of formation in Table 53 to calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CuOs.
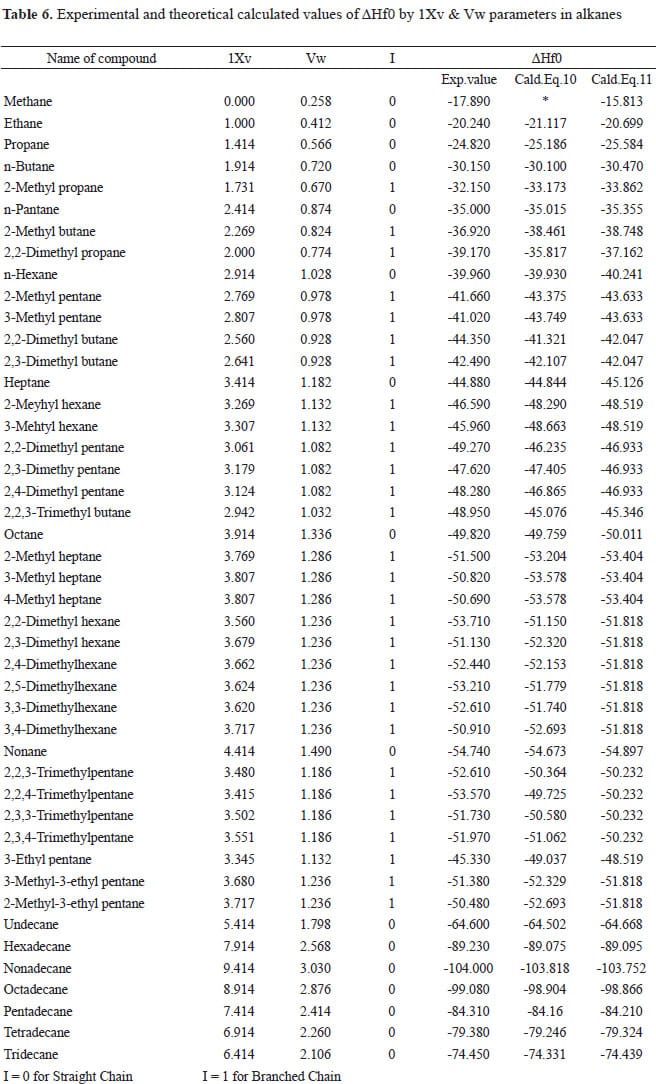
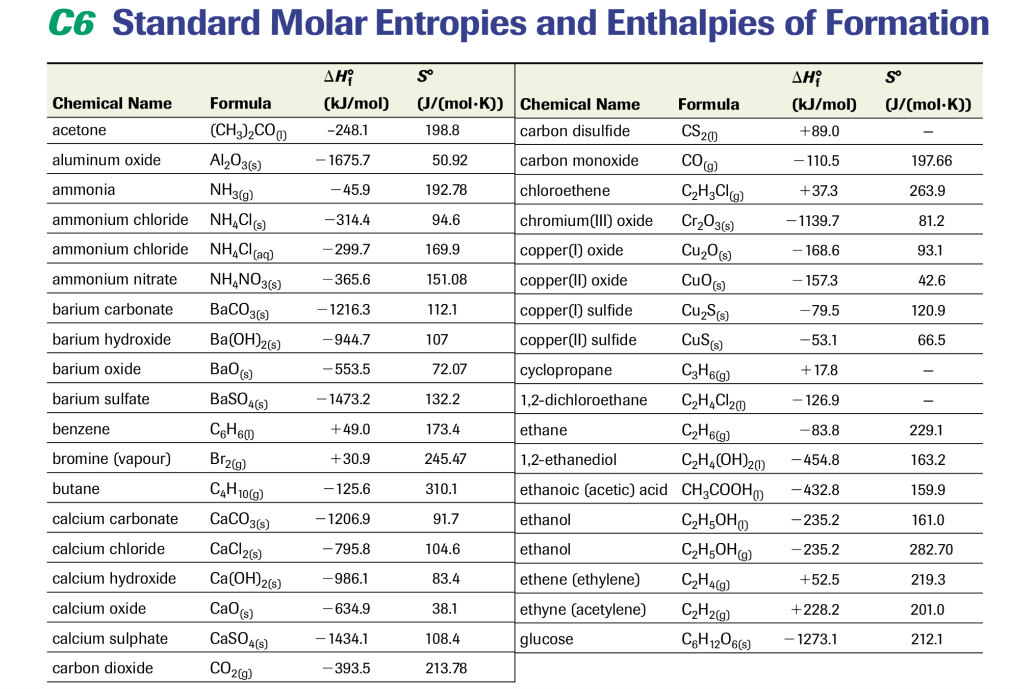
Table 147 is a separate table for unbranched hydrocarbons. Enthalpy of formation is basically a special case of standard enthalpy of reaction where two or more reactants combine to form one mole of the product. Atomization of dihydrogen molecule.
Cgraphites2H2g CH4g C g r a p h i t e s 2 H 2 g C H 4 g. 22 rows Standard Enthalpy of Formation for Atomic and Molecular Ions Cations ΔH f kJmol Cations ΔH. CuOs H 2 g Cus H 2 Ol ΔH 1297 kJ.
This equation essentially states that the standard enthalpy change of formation is equal to the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the products minus the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants. ΔfH Δ f H 7481kJ mol1 7481 k J m o l 1. Use the following mean bond enthalpy data to calculate the enthalpy of formation of NH3 ½ N2 15 H2 NH3 note the balancing is to agree with the definition of heat of formation ie.
Trends in enthalpies of formation Table 4 are not as regular as those of lattice energy. Standard Enthalpy of Formation Examples. And the standard enthalpy of formation values.
Earhart 1172016 Substance ΔH f kJmol Substance ΔH f kJmol Substance ΔH f kJmol AgCls -1270 CaSO 4s -14345 N 2H 4g 954 Al 2O 3s-16757 Fe 2O 3s -8242 N 2H 4l 506 CHCl 3g -1032 HBrg -364 N 2Og 821 CH 2Cl 2g -955 HClg -923 N 2O 4g 91 CH. 43 rows Also called standard enthalpy of formation the molar heat of. 378 rows The standard enthalpy of formation ΔH 0 f of a compound is the change in.
One mole of product ENN 944 kJ mol-1 EH-H 436 kJ mol-1 EN-H 388 kJ mol-1 H bond energies broken - bond energies made. Thermodynamic data at 25oC for assorted organic substances. Standard Enthalpies Free Energies of Formation Standard Entropies Author.
They are compiled in huge tables of thermodynamic quantities. Hans Lohninger This table lists the standard enthalpies ΔH the free energies ΔG of formation of compounds from elements in their standard states and the thermodynamic third-law entropies S of compounds at 298 K. H 2 g 2H g.
Give the equation for the enthalpy of formation of sulfuric acid. ½N2g O2g NO2g Cas ½O2g CaOs Cgraphite 2Br2l CBr4s 4. The enthalpy change for this reaction can be called the enthalpy of formation of water Ay H20.
H 2 g Ss 2O 2 g H 2 SO 4 l ΔHf -811 kJ mol-1. These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical reactions that are impractical or dangerous to carry out or for. Δ a H 0 4350 kJ mol -1.